what would happen to life on earth if the rates of photosynthesis and cellular respiration
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the chemical process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use the energy from sunlight to transform carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) from the temper, and water, into organic compounds such equally sugars. These sugars are and then used to brand complex carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, as well as the wood, leaves, and roots of plants. The amount of organic matter made by photosynthesizing organisms in an ecosystem is defined as the productivity of that ecosystem. Free energy flows through the biosphere equally organisms (including some animals) eat photosynthesizing organisms (called herbivores), and as organisms then swallow those herbivores (carnivores), etc., to get their energy for growth, reproduction, and other functions. This free energy is acquired through the procedure of cellular respiration, which usually requires oxygen.Oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis. About 70% of the oxygen in the temper that nosotros breathe comes from algae in the ocean. Atmospheric oxygen from photosynthesis also forms the ozone layer, which protects organisms from harmful high-energy ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. Because photosynthesis also requires water, the availability of water affects the productivity and biomass of the ecosystem, which in plough affects how much and how speedily water cycles through the ecosystem.
Fossil fuels are derived from the burial of photosynthetic organisms, including plants on land (which primarily grade coal) and plankton in the oceans (which primarily form oil and natural gas). While buried, the carbon in the organic material is removed from the carbon cycle for thousands of years to hundreds of millions of years. The burning of fossil fuels has dramatically increased the substitution of carbon from the ground back into the atmosphere and oceans. This return of carbon dorsum into temper equally carbon dioxide is occurring at a rate that is hundreds to thousands of times faster than it took to bury it, and much faster than it can exist removed past photosynthesis or weathering. Thus, the carbon dioxide released from the called-for of fossil fuels is accumulating in the atmosphere, increasing boilerplate temperatures and causing ocean acidification.
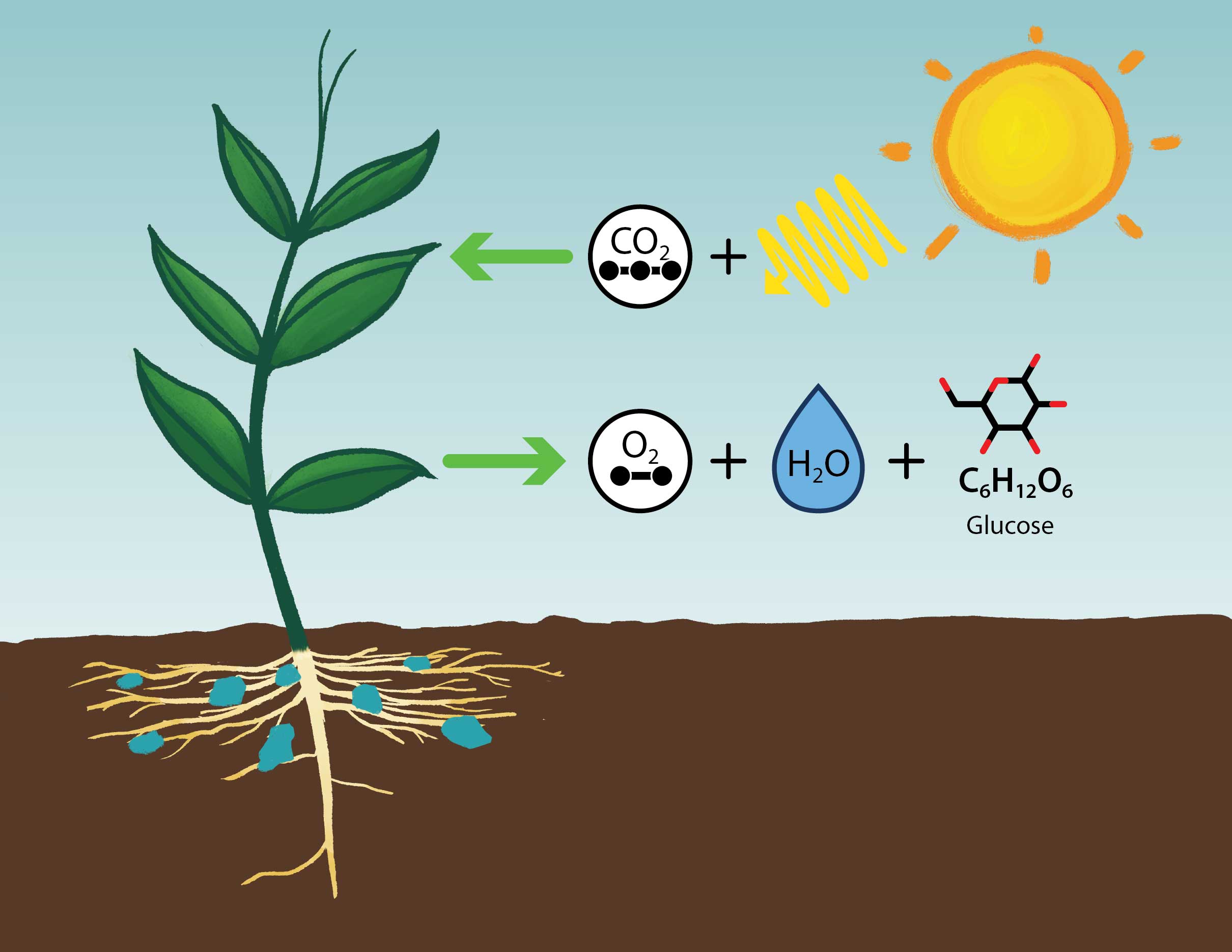
A simplified diagram showing the overall inputs – carbon dioxide, h2o, and sunlight, and products
– oxygen and sugar (glucose), of photosynthesis.
The charge per unit of photosynthesis in ecosystems is affected by various ecology conditions, including:
- Climatic conditions, such equally the amount of sunlight available at different latitudes, temperature, and precipitation For case, ecosystems at depression latitudes, such every bit tropical rainforests, take college productivity and biomass than ecosystems nearly the poles because of they receive more sunlight and rainfall than regions at higher latitudes.
- Nutrients, specially nitrogen and phosphorus, which when limited tin decrease productivity, but when arable can increase productivity and biomass. Photosynthesizing organisms extract nutrients from the surroundings, and return them to the soil when they dice and decay.
- Numerous other abiotic environmental factors, including soil quality (oftentimes related to food levels), wildfires, water acidity, and oxygen levels.
- Species interactions, including the resources species provide for each other, and how they compete for resources such as water, light, and/or space. Species that reduce or increase the success of other species modify population sizes, thus affecting productivity and biomass.
- Evolutionary processes that tin can change the growth and reproduction rates of photosynthesizing organisms over time, as well equally the growth and reproduction of rates of the organisms that eat them.
Humans take contradistinct the rate of photosynthesis, and in turn productivity, in ecosystems through a diverseness of activities, including:
- Deforestation, habitat destruction, and urbanization, which remove plants and copse from the environment and disrupt ecosystems.
- Agricultural activities that increase the amount of crops available to feed the growing global human population.
- The apply of fertilizers for agricultural activities that increase the amount of nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorous, in soil or water. These nutrients increment establish and algae growth, including growth of species that are toxic to other organisms. Increased nutrients is non always a good thing. For example, in aquatic environments, nutrient-rich runoff tin can cause large amounts of algae to grow – when these algae dice, they are consumed by leaner which tin can reduce oxygen levels in the water, killing fish and other species. This procedure is known every bit eutrophication.
- Human freshwater apply, which can limit the amount of water available for plants and trees in an ecosystem.
- The release of pollutants and waste, which can reduce growth and reproduction or impale plants.
- Activities that release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that crusade global warming, such as the burning of fossil fuels, agricultural activities, and deforestation. Increasing carbon dioxide levels may increment photosynthesis rates in some plants, but this can also make plants less nutritious. Increasing average global land and sea temperatures and changes in atmospheric precipitation patterns also touch on establish and algae growth, and can brand certain species more susceptible to illness.
- Activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, agricultural activities, and deforestation that release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which is captivated by the body of water causing acidification. The decreasing pH of ocean waters (along with bounding main warming) causes physiological stress for many found and algae species, which can decrease growth, reproduction, species population sizes, and biomass.
- Introducing invasive species that compete with native plant or algae species for nutrients, water, light, or other resource, reducing native species populations.
Earth system model about photosynthesis
The Globe arrangement model below includes some of the processes and phenomena related to photosynthesis. These processes operate at various rates and on different spatial and temporal scales. For case, carbon dioxide is transferred among plants and animals over relatively short time periods (hours-weeks), only the deforestation alters ecosystems over decades to centuries, or longer. Tin can you think of additional cause and effect relationships between photosynthesis and other processes in the Earth organisation?
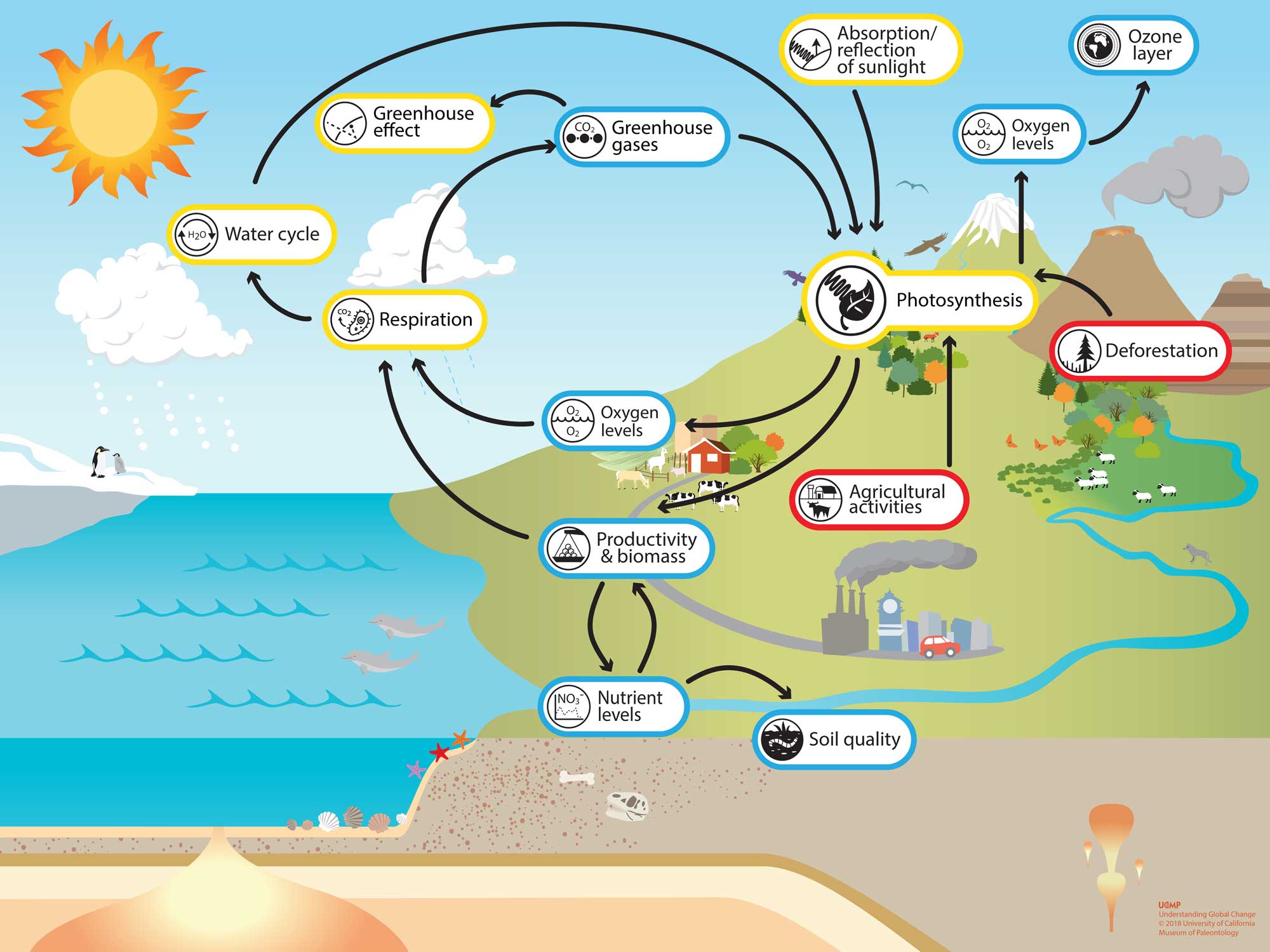
Explore the Earth Organisation
Click the bolded terms (eastward.one thousand. respiration, productivity and biomass, and burning of fossil fuels) on this page to acquire more almost these process and phenomena. Alternatively, explore the Understanding Global Change Infographic and discover new topics that are of interest and/or locally relevant to you.
Investigate
Learn more in these real-globe examples, and challenge yourself to construct a model that explains the Globe arrangement relationships.
- The bacteria that changed the world
Links to Learn More than
- New York Times: 'Global Greening' Sounds Good. In the Long Run Information technology'due south Terrible
- USGCRP: Climate and Health Assessment, Nutrient Condom, Nutrition, and Distribution
- HHMI BioInteractive: Photosynthesis
Source: https://ugc.berkeley.edu/background-content/photosynthesis/
0 Response to "what would happen to life on earth if the rates of photosynthesis and cellular respiration"
Post a Comment